

Types of fallout Atmospheric nuclear weapon tests almost doubled the concentration of radioactive 14C in the Northern Hemisphere, before levels slowly declined following the Partial Test Ban Treaty.įallout comes in two varieties.
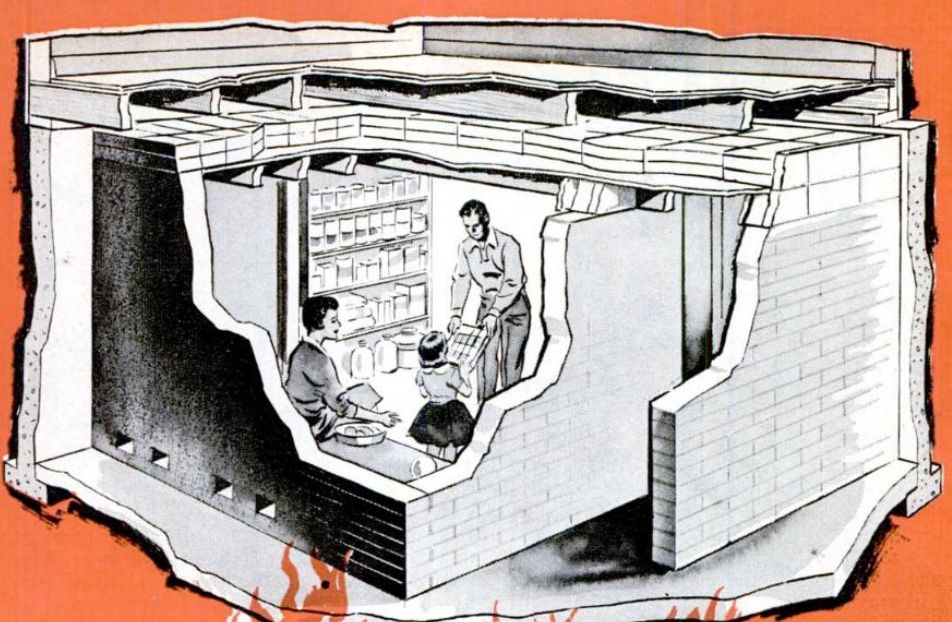
This radioactive dust, usually consisting of fission products mixed with bystanding atoms that are neutron-activated by exposure, is a form of radioactive contamination. Fallout may get entrained with the products of a pyrocumulus cloud and fall as black rain (rain darkened by soot and other particulates, which fell within 30–40 minutes of the atomic bombings of Hiroshima and Nagasaki). The amount and spread of fallout is a product of the size of the weapon and the altitude at which it is detonated. It commonly refers to the radioactive dust and ash created when a nuclear weapon explodes.
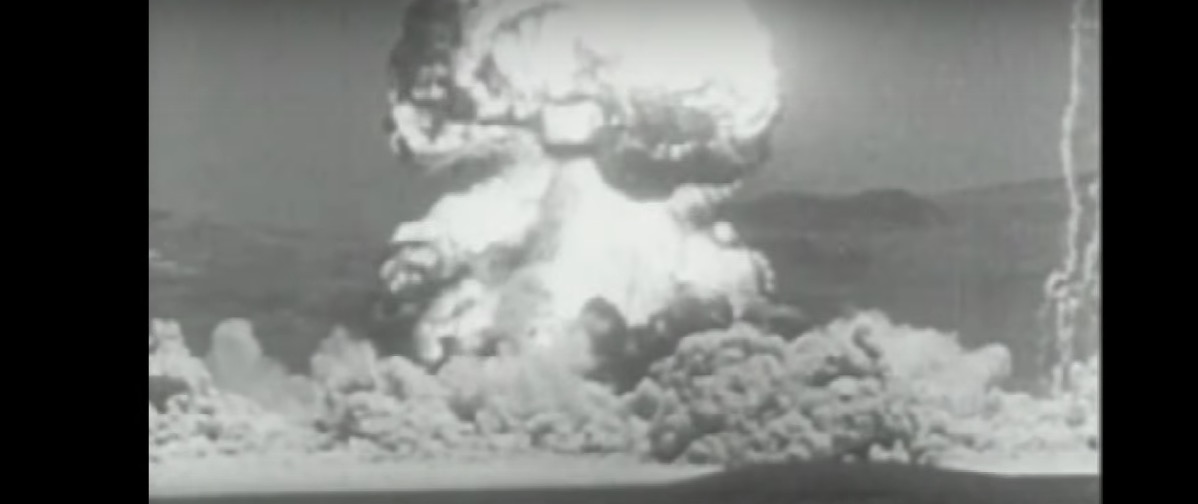

Nuclear fallout is the residual radioactive material propelled into the upper atmosphere following a nuclear blast, so called because it "falls out" of the sky after the explosion and the shock wave has passed.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
